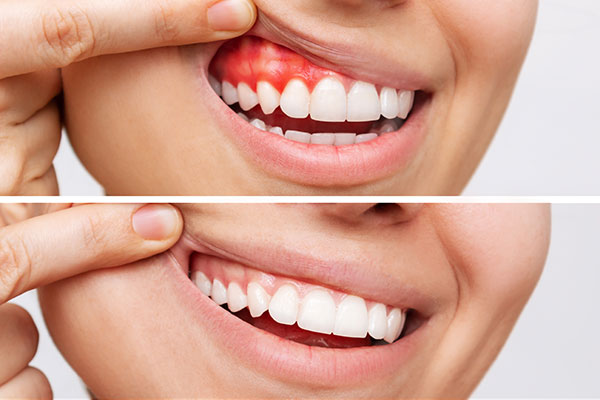
Stages of Gum Disease
Protecting Your Smile: Early Intervention for Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a progressive condition that can lead to tooth loss and other serious health complications when left untreated. Gum disease develops in stages, starting with gingivitis and progressing to periodontitis.
Understanding the stages of periodontal disease and its symptoms is essential for early detection and effective treatment. To schedule an appointment, contact our dentist in Ashland today by calling (541) 482-7771.
Gum Disease Stages
Gingivitis
The earliest stage of periodontal disease is gingivitis, which is a mild inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup around the teeth. Symptoms of gingivitis include:
- Bleeding gums
- Swollen gums
- Tender or sensitive gums
- Bad breath
- Receding gums
- Gum sensitivity
- Changes in gum texture
Fortunately, gingivitis can often be reversed with proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and regular dental cleanings.
If you have noticed signs of gingivitis, schedule an appointment with our dentist as soon as possible. With early intervention, gingivitis can be easily treated before it progresses to more severe stages of gum disease.
Early Periodontitis
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to early periodontitis, which is characterized by a more significant infection that begins to affect the bone supporting the teeth.
Symptoms of early periodontitis include:
- Persistent bad breath
- Bleeding gums
- Swollen or red gums
- Gum recession
- Tooth Sensitivity
- Loose teeth
- Formation of periodontal pockets
At this stage of gum disease, the bacteria have begun to penetrate the deeper layers of gum tissue and the surrounding bone itself, causing irreversible damage and bone loss.
To treat early periodontitis, dentists may recommend scaling and root planing, which involves removing plaque and tartar buildup from beneath the gum line and smoothing the tooth root surfaces.
Moderate Periodontitis
Moderate periodontitis is the third stage of gum disease, and it’s characterized by significant bone loss and gum recession. Other symptoms include:
- Deep gum pockets
- Gum swelling and redness
- Tooth migration or shifting
- Gum abscesses
- Chronic bad breath
- Changes in the bite
- Pain or discomfort while chewing
Treatment for moderate periodontitis typically involves a combination of scaling and root planing, antibiotic therapy, and possible surgical intervention. Dentists may recommend a bone graft or guided soft tissue regeneration procedure to help regenerate lost bone and gum tissue.
Advanced Periodontitis
The final stage of gum disease is advanced periodontitis, which is characterized by severe bone loss and tooth mobility. At this severe stage, teeth may need to be extracted, and patients may require extensive reconstructive procedures to restore their oral health.
Symptoms of advanced periodontitis include:
- Severe pain
- Tooth loss
- Gum inflammation
- Severe gum recession
- Pus discharge and painful abscesses
- Swollen or bleeding gums
You must seek professional dental care if you’re experiencing the symptoms of advanced periodontal disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can gum disease be cured?
While more advanced stages of gum disease can’t be completely cured, they can be managed and controlled through proper oral hygiene practices and professional dental care. With early intervention, gingivitis can often be reversed, and the progression of gum disease can be slowed or stopped.
How long until gum disease is irreversible?
Gum disease becomes irreversible in the second and third stages. To avoid either moderate periodontitis or advanced periodontitis, maintain good oral hygiene and visit the dentist regularly.
Can gum disease affect my overall health?
Yes, there’s growing evidence to suggest that gum disease may be linked to several systemic health conditions, including heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. This is because the bacteria that cause gum disease can enter the bloodstream and potentially cause inflammation throughout the body. Managing your gum health is an important part of maintaining your overall health and well-being.
How fast does periodontal disease progress?
Periodontal disease progresses gradually yet consistently. Within just four days, the plaque buildup can reach its peak, allowing visible signs of gingivitis to appear by day five. If gingivitis is left untreated, more advanced periodontal disease can manifest in a matter of weeks.
Are You at Risk for Gum Disease? Schedule a Consultation!
If you’re experiencing symptoms of gum disease or want to learn more about how to prevent it, schedule an appointment with our Ashland dentist today. Don’t let gum disease go untreated and risk the potential for serious health complications.
Contact us at (541) 482-7771 to schedule your appointment and take the first step toward achieving optimal oral health.